Fixing Common Windows Errors Windows is one of the most popular operating systems worldwide, but like any software, it has its fair share of errors. These errors can interrupt your workflow, slow down your computer, and even cause data loss if left unresolved. Fortunately, many of these issues can be fixed in minutes, even by non-tech-savvy users. In this guide, we’ll walk through simple solutions to some of the most common Windows errors.
What Causes Windows Errors?
Windows errors can be triggered by various factors:
- Outdated drivers
- Corrupted files or settings
- Insufficient memory or storage
- Malware or virus infections
- Conflicting software
Understanding the cause can help you troubleshoot the error faster.
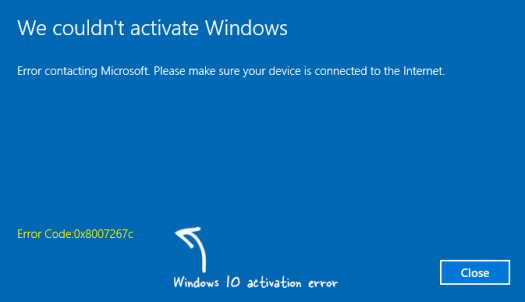
1. “Blue Screen of Death” (BSOD)
Description: The BSOD is a critical error that forces Windows to shut down unexpectedly, usually due to hardware or driver issues.
Solution:
- Restart your computer and see if the issue persists.
- Check for updates: Install any available Windows updates.
- Update drivers: Outdated drivers can cause compatibility issues.
- Run the Troubleshooter: Go to Settings > Update & Security > Troubleshoot > Blue Screen to use Windows’ built-in BSOD troubleshooting tool.
2. “Application Not Responding”
Description: This error occurs when an application becomes unresponsive, often due to high memory usage or a corrupted file.
Solution:
- End the Task: Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager. Right-click the unresponsive application and select “End Task.”
- Clear Temporary Files: Remove unnecessary files by typing Disk Cleanup in the search bar and selecting the disk you want to clean.
- Reinstall the Application: If the issue persists, reinstalling the app can often fix bugs or corrupted files.
3. “Windows Update Error”
Description: Sometimes, Windows updates fail due to network issues or corrupted system files.
Solution:
- Run the Windows Update Troubleshooter: Go to Settings > Update & Security > Troubleshoot > Windows Update.
- Clear Update Cache: Stop the Windows Update service by typing
services.mscin the search bar. Locate Windows Update, right-click, and select “Stop.” Then delete the contents of theC:\Windows\SoftwareDistributionfolder. - Restart and Retry: Restart your computer and try updating again.
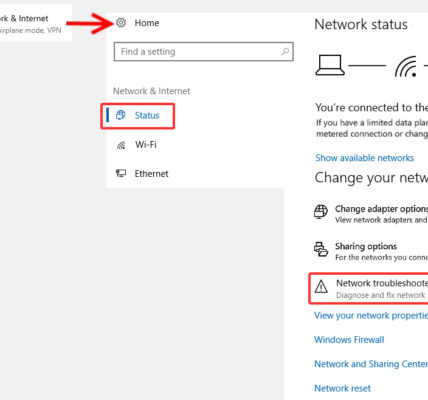
4. “No Internet, Secured” Error
Description: This error indicates your computer is connected to Wi-Fi but lacks internet access.
Solution:
- Restart Your Router: Sometimes a simple router restart can resolve connection issues.
- Run Network Troubleshooter: Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Status > Network Troubleshooter.
- Update Network Drivers: In Device Manager, find Network Adapters, right-click your adapter, and select “Update driver.”
5. “Windows Cannot Find…” Error
Description: This message appears when Windows cannot locate a file or application, often due to incorrect file paths.
Solution:
- Check the File Path: Make sure the file or folder path is correct.
- Use File Explorer Search: Type the file name in File Explorer’s search bar to locate it.
- Recreate Shortcuts: Delete and recreate the shortcut if you’re getting this error with a specific shortcut.
6. “DLL Not Found” Error
Description: Missing or corrupt DLL (Dynamic Link Library) files prevent applications from running properly.
Solution:
- Reinstall the Program: Reinstalling the application that triggered the error can often replace missing DLL files.
- Use Windows System File Checker (SFC): Open Command Prompt as an administrator and type
sfc /scannow. - Download the DLL: In some cases, you can manually download the missing DLL file from a reliable source. However, use caution with third-party sites.
7. “Low Disk Space” Error
Description: This error appears when your disk is nearly full, which can slow down your system.
Solution:
- Delete Unnecessary Files: Use Disk Cleanup or delete large files and applications you don’t need.
- Clear Temporary Files: Clear temporary and cache files by pressing Win + R, typing
%temp%, and deleting the contents of the folder. - Move Files to External Storage: Transfer large files, such as photos or videos, to an external drive.
8. “Device Not Recognized” (USB)
Description: This error occurs when Windows cannot detect a USB device.
Solution:
- Try a Different Port: Switch the USB device to a different port.
- Update USB Drivers: In Device Manager, right-click the USB device, select “Update driver.”
- Reinstall USB Controllers: Uninstall the USB drivers and restart your computer. Windows will reinstall them automatically.
9. “Printer Offline” Error
Description: This error appears when Windows cannot connect to your printer.
Solution:
- Check Printer Connection: Ensure the printer is on and connected to the same network.
- Run Printer Troubleshooter: Go to Settings > Devices > Printers & scanners > select your printer > Run the troubleshooter.
- Reinstall Printer Drivers: Go to Device Manager, locate your printer, and reinstall its drivers.
10. “Windows Cannot Boot” Error
Description: If Windows fails to boot, it can be caused by corrupted boot files or hardware issues.
Solution:
- Use Startup Repair: Insert a Windows installation disk, select Repair your computer > Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Repair.
- Check Boot Order: Ensure your hard drive is set as the first boot option in BIOS.
- Restore from a Backup: If you have a backup, restore your system to a previous working state.
11. “Access Denied” Error
Description: This error typically appears when you lack permission to access a folder or file.
Solution:
- Take Ownership of the File: Right-click the file or folder, select Properties > Security > Advanced > Change owner to yourself.
- Grant Permissions: In the Security tab, add or modify permissions to allow full control.
- Check File Encryption: Some files are restricted by encryption. Make sure you have access.
12. “Sound Not Working”
Description: Audio errors can arise from driver issues or incorrect sound settings.
Solution:
- Check Sound Settings: Right-click the volume icon, select “Open Sound settings,” and make sure the correct device is selected.
- Update Audio Drivers: In Device Manager, find and update your audio drivers.
- Troubleshoot Audio: Use the built-in troubleshooter in Sound settings.
13. “Wi-Fi Disconnects Frequently”
Description: Frequent Wi-Fi drops can be due to network settings or driver issues.
Solution:
- Restart Router and Device: Power cycle your router and reconnect.
- Forget and Reconnect Network: Forget the Wi-Fi network and reconnect with the password.
- Update Network Drivers: Ensure your Wi-Fi drivers are up-to-date.
Fixing Common Windows Errors
Windows errors are inevitable, but most of them have straightforward fixes. With a little patience, you can resolve common issues without professional help. By regularly updating your system, cleaning out old files, and following these troubleshooting steps, you’ll keep your computer running smoothly.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the best way to clean my disk space?
Use Disk Cleanup, uninstall unused programs, and delete large or duplicate files.
How can I prevent Windows errors?
Keep your system updated, install reputable antivirus software, and avoid downloading files from untrusted sites.
Is it safe to use third-party software to fix Windows errors?
Be cautious; only use software from reputable developers to avoid malware risks.
What should I do if none of these fixes work?
If you’ve tried everything and the error persists, contact professional tech support.
Can updating Windows cause errors?
Sometimes, updates may cause compatibility issues. It’s best to back up your data before updating.