Troubleshooting Network Issues on Windows. Dealing with network issues on Windows can be frustrating, especially when you’re trying to get work done or stay connected. Thankfully, most problems can be resolved with simple steps. Here’s a guide to troubleshooting and fixing common network issues on Windows.
Check Your Network Connection
Before diving into advanced solutions, ensure your device is connected to a network.
- Verify Wi-Fi or Ethernet Status:
- Look at the network icon in the taskbar.
- If there’s a red X or warning symbol, you’re not connected.
- Reconnect to Wi-Fi:
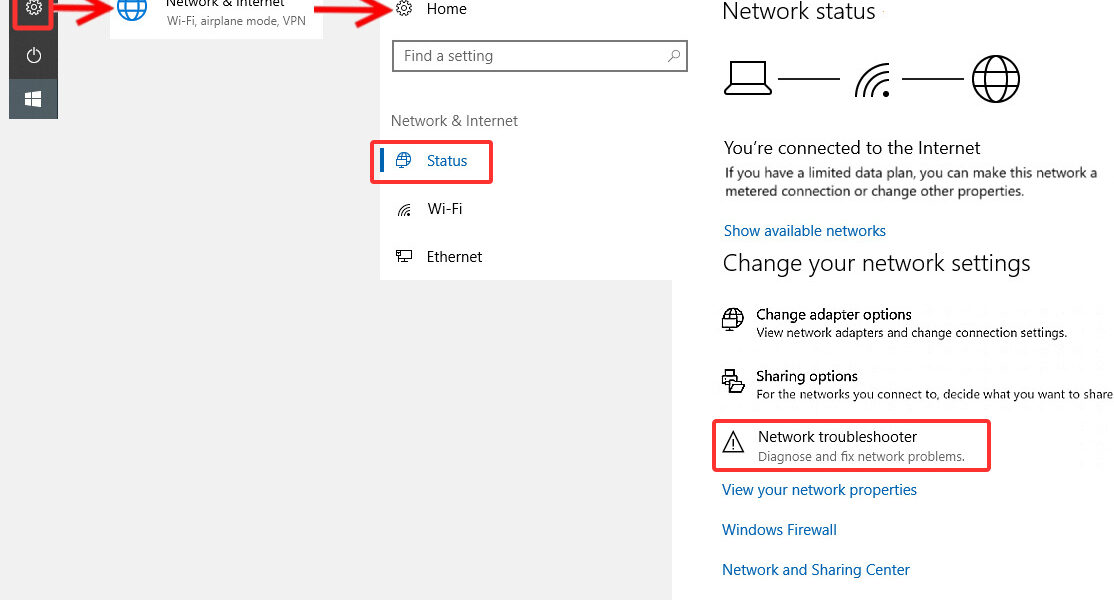
- Open the Network & Internet Settings.
- Select your Wi-Fi network and click Connect.
- Check the Physical Connection (For Ethernet):
- Ensure the Ethernet cable is properly plugged into your computer and router.
Restart Your Router and PC
Sometimes, a simple restart can fix the issue.
- Restart the Router:
- Turn off your router.
- Wait for 10-15 seconds and turn it back on.
- Restart Your PC:
- Click the Start menu, select Power, and choose Restart.
Use the Windows Network Troubleshooter
Windows provides a built-in troubleshooter to diagnose and fix network problems.
- Open the Troubleshooter:
- Right-click the network icon in the taskbar and select Troubleshoot Problems.
- Follow the on-screen instructions.
- Review Results:
- If the troubleshooter identifies an issue, it will attempt to fix it automatically or provide steps to resolve it.
Check Your Network Settings
Incorrect settings can cause connectivity problems.
- Verify IP and DNS Settings:
- Go to Control Panel > Network and Sharing Center > Change Adapter Settings.
- Right-click your connection and select Properties.
- Ensure Obtain an IP address automatically and Obtain DNS server address automatically are selected.
- Reset Network Settings:
- Open Settings, go to Network & Internet > Status, and click Network Reset.
- Restart your PC after the reset.
Update Network Drivers
Outdated or corrupted network drivers can lead to connectivity issues.
- Open Device Manager:
- Press Windows + X and select Device Manager.
- Update Driver:
- Expand Network Adapters.
- Right-click your network adapter and choose Update Driver.
- Select Search automatically for updated driver software.
- Reinstall the Driver:
- If updating doesn’t work, uninstall the driver and restart your PC. Windows will reinstall the driver automatically.
Check Firewall and Antivirus Settings
Sometimes, firewalls or antivirus programs can block your connection.
- Disable Firewall Temporarily:
- Go to Control Panel > Windows Defender Firewall > Turn Windows Defender Firewall on or off.
- Turn it off temporarily and test your connection.
- Check Antivirus Settings:
- Open your antivirus software and look for any network-related blocks.
- Temporarily disable the antivirus and see if the connection improves.
Flush DNS and Reset TCP/IP
Network issues can sometimes stem from DNS or IP conflicts.
- Open Command Prompt:
- Press Windows + R, type
cmd, and press Enter.
- Press Windows + R, type
- Run Network Commands:
- Type the following commands one at a time and press Enter after each:
ipconfig /flushdnsnetsh int ip resetnetsh winsock reset
- Type the following commands one at a time and press Enter after each:
- Restart Your PC:
- Restart your computer for changes to take effect.
Test Your Connection
If your network is still not working, testing it can help pinpoint the issue.
- Ping the Router:
- Open Command Prompt and type
ping 192.168.1.1(or your router’s IP address). - If you get replies, your PC can communicate with the router.
- Open Command Prompt and type
- Check Internet Access:
- Type
ping google.com. - If there are no replies, the problem might be with your ISP.
- Type
Contact Your Internet Service Provider
If all else fails, the issue might be with your ISP.
- Check for Outages:
- Contact your ISP or check their website for outage notifications.
- Ask for Assistance:
- Provide details of your troubleshooting steps to their support team for faster help.
Tips for Troubleshooting Network Issues on Windows
- Keep Your Drivers Updated: Regularly update your network drivers.
- Secure Your Network: Use strong passwords for Wi-Fi to avoid unauthorized access.
- Restart Periodically: Restart your router occasionally to keep it functioning optimally.
- Monitor Signal Strength: Ensure your device is within range of the Wi-Fi signal.
By following these steps, you can resolve most network problems on Windows. A little patience and systematic troubleshooting can save you from hours of frustration!